What is PCB?
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Boards and it is heart of all the electronics. Like You’ve probably seen a green color board in any kind of Electronics gadgets i.e. TV, Refrigerator, Mobile, Computers, TV Remotes and etc. that’s the PCB. Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a foundational component in electronics, providing a mechanical base for mounting and electrically connecting electronic components. PCBs consist of conductive pathways (traces) etched onto an insulating substrate, allowing electrical signals to flow between components. They are used in virtually all electronic devices, from simple gadgets to complex computers and industrial equipment. PCBs are most commonly made out of fiberglass, composite epoxy, or another composite material.Before PCBs were introduced, components were connected manually with wires — which was messy, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Modern PCBs have revolutionized electronics by making circuits more compact, reliable, and manufacturable.
Evolution of PCB Design
Before PCBs
- Components were connected using wires and soldered point-to-point
- Complex, time-consuming, and prone to errors
Modern PCBs
- Use copper traces for connectivity
- Allow automation, design precision, and mass production
(Below Image will give you more clarity)
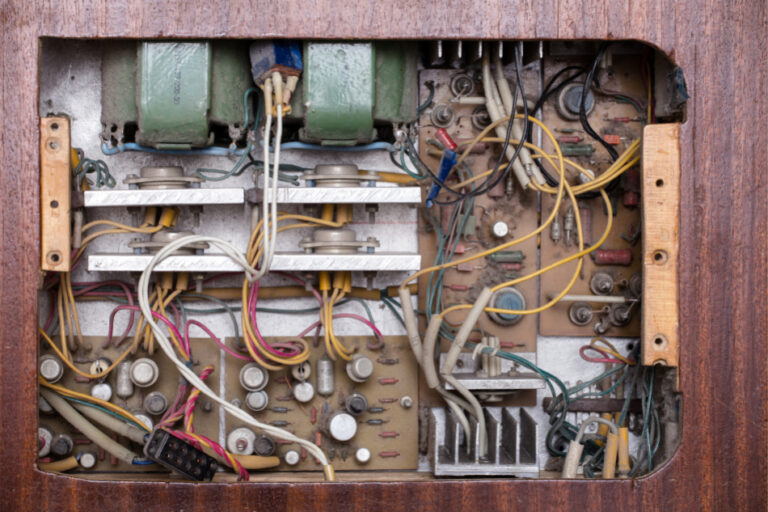
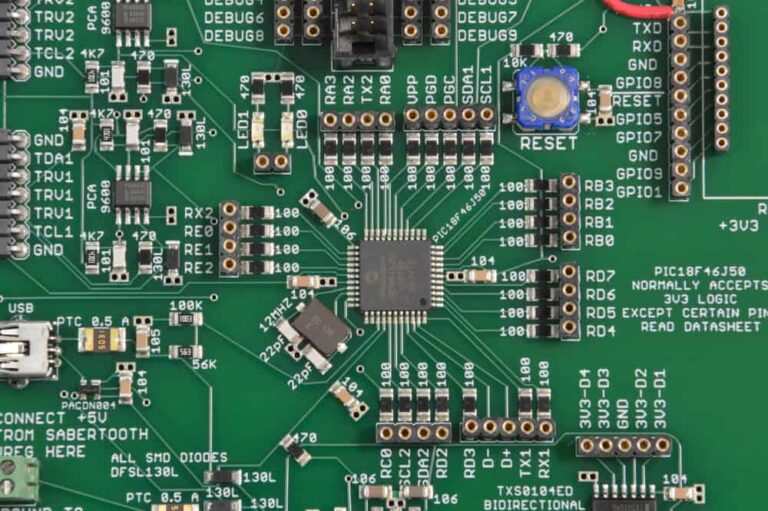
Why PCB Design Matters
Many beginners start with breadboards and perf boards for prototyping. While these are great for testing ideas quickly, they aren’t suitable for final products due to issues like:
- Loose connections
- Signal integrity problems
- Poor aesthetics and mechanical support
- Difficult scalability
PCB design eliminates these problems by allowing precise control over the layout, grounding, shielding, and thermal management of components.
Key Functions of PCB.
- Mechanical Support – Holds components in place
- Electrical Connectivity – Routes signals and power between components
- Signal Integrity – Maintains the quality and timing of signals
- Thermal Management – Helps dissipate heat through copper layers or thermal vias
Types of PCB
There are several types of PCBs based on construction and application:
- Single-sided PCB – Copper on one side only, and Components will be mounted on the other side.
- Double-sided PCB – Copper on both top and bottom
- Multilayer PCB – Multiple layers of copper sandwiched between insulating layers and components can be on both sides, depending on the type of components, i.e., Through-hole and SMD
- Rigid PCB – Solid and inflexible, and generally, you will see it in major devices.
- Flexible PCB – Can bend or fold
- Rigid-Flex PCB – Combination of rigid and flexible sections. Each type has its use case in consumer, industrial, automotive, or medical electronics.
Tools for PCB Design
♦ Beginner/Open-source tools
- KiCad: Free. Open-source and suitable for both hobbyists and professionals.
- Autodesk EAGLE: Paid. Offers a free version with limitations on board size and features. Note that the free/Lite version is no longer offered, and Fusion for personal use is the suggested path forward.
- EasyEDA: Free. A web-based platform with paid services for advanced features and larger projects.
- Fritzing: Free. Binaries are available at a cost, while the source code is free under the GPL 3.0 license.
- CircuitMaker: Free. Based on Altium Designer technology and designed for the maker community.
♦ Professional/Advanced tools
- Altium Designer: Paid. Offers flexible licensing options, including subscription and perpetual licenses.
- Cadence Allegro: Paid. Features both perpetual and subscription licenses. A free 30-day trial is available.
- Siemens PADS: Paid. Free trial available.
- OrCAD: Paid. Free 30-day trial for professionals and a 6-month trial for students are available.
- Zuken CR-8000: Paid. Pricing information is available upon request through a quote.
Conclusion
In this post, you would have understood the overview of the Printed Circuit Board and types of PCB, PCB Design tools for beginners to professionals, and the Key Function Area. In this series of Posts, I’ll cover everything about PCB from concept to schematic, Layout, Assembly, and Fabrication.